March 14th marks World Kidney Day, a day dedicated to raising awareness about the importance of kidney health and the prevention of kidney diseases worldwide. At B. P. Poddar Hospital & Medical Research Limited, we are proud to join the global community in advocating for kidney health and spreading crucial awareness about kidney diseases and their prevention.
The Significance of Kidney Health:
The kidneys are vital organs responsible for filtering waste and excess fluids from the blood, regulating blood pressure, producing red blood cells, and maintaining electrolyte balance. Despite their importance, kidney diseases often go undetected until they reach advanced stages, highlighting the critical need for proactive kidney care and awareness.
Addressing the Global Burden:
Kidney diseases affect millions of people globally, with chronic kidney disease (CKD) being a significant concern. Factors such as diabetes, hypertension, obesity, and unhealthy lifestyle choices contribute to the rising prevalence of kidney diseases. Early detection, lifestyle modifications, and timely intervention are key to mitigating the burden of kidney diseases and improving outcomes.
Our Commitment to Kidney Health:
At B. P. Poddar Hospital & Medical Research Limited, we are committed to providing comprehensive kidney care services encompassing prevention, diagnosis, treatment, and ongoing management. Our team of skilled nephrologists, urologists, and healthcare professionals work tirelessly to deliver personalized care tailored to the unique needs of each patient.
Empowering Through Education:
Education plays a pivotal role in promoting kidney health and preventing kidney diseases. Through community outreach programs, educational seminars, and digital campaigns, we aim to empower individuals with knowledge about kidney health, risk factors, and preventive measures. By fostering awareness and understanding, we empower individuals to take proactive steps towards maintaining optimal kidney health.
Innovative Solutions for Better Outcomes:
Innovation is key to advancing kidney care and enhancing patient outcomes. At B. P. Poddar Hospital & Medical Research Limited, we leverage state-of-the-art technology, advanced diagnostics, and minimally invasive treatments to provide cutting-edge care to our patients. Through ongoing research and collaboration, we strive to develop innovative solutions that address the evolving challenges in kidney health.
Join Us in Making a Difference:
As we observe World Kidney Day, we urge everyone to prioritize kidney health and take proactive steps towards prevention and early detection of kidney diseases. Whether through regular health screenings, adopting a healthy lifestyle, or raising awareness in our communities, each of us can contribute to the fight against kidney diseases.
Together, Let's Make Kidney Health a Priority:
At B. P. Poddar Hospital & Medical Research Limited, we stand committed to promoting kidney health, advancing research, and delivering compassionate care to those in need. Join us in our mission to prioritize kidney health and ensure a brighter, healthier future for all.
For more information about our kidney care services or to schedule a consultation, please visit our website or contact us directly. Together, let's work towards a world where kidney health is valued, protected, and prioritized.Obesity is a complex, multifactorial condition that affects millions of people worldwide, posing significant health risks and challenges. On World Obesity Day, observed annually on March 4th, it's crucial to raise awareness about this global epidemic, its causes, consequences, and preventive measures. At B. P. Poddar Hospital & Medical Research Limited, we recognize the importance of addressing obesity as a critical public health issue and are committed to providing support, education, and treatment to individuals affected by it.
The prevalence of obesity has been steadily increasing over the years, reaching alarming levels in many countries. Sedentary lifestyles, unhealthy dietary habits, genetic factors, socioeconomic status, and environmental influences all contribute to the rising rates of obesity. It is not merely a cosmetic concern but a serious medical condition associated with various health complications, including type 2 diabetes, heart disease, stroke, certain types of cancer, and mental health disorders.
One of the most effective ways to combat obesity is through education and prevention. Promoting healthy eating habits, regular physical activity, and lifestyle modifications can significantly reduce the risk of obesity and its related diseases. Additionally, early intervention and access to quality healthcare services are essential for managing obesity and preventing its complications.
At B. P. Poddar Hospital & Medical Research Limited, we offer comprehensive obesity management programs tailored to the individual needs of our patients. Our multidisciplinary team of healthcare professionals, including dietitians, physiotherapists, psychologists, and bariatric surgeons, work collaboratively to provide personalized care and support throughout the weight loss journey.
Our approach to obesity management focuses on a combination of dietary counseling, exercise prescription, behavior modification, and, when appropriate, surgical interventions such as bariatric surgery. We emphasize the importance of sustainable lifestyle changes and empower our patients to take control of their health and well-being.
In addition to clinical services, we also prioritize community outreach and education initiatives to raise awareness about obesity and its associated risks. Through seminars, workshops, and online resources, we aim to educate individuals about the importance of healthy living and provide practical tips for maintaining a balanced diet and active lifestyle.
Furthermore, we advocate for policy changes and public health interventions aimed at creating environments that support healthy choices and promote physical activity. This includes initiatives to improve access to nutritious foods, create safe spaces for exercise, and regulate the marketing of unhealthy products.
On World Obesity Day, let us reaffirm our commitment to tackling this global epidemic and supporting those affected by it. Together, we can make a difference in the fight against obesity and build healthier, more resilient communities for future generations. At B. P. Poddar Hospital & Medical Research Limited, we stand ready to provide compassionate care, innovative treatments, and ongoing support to individuals striving to achieve and maintain a healthy weight.On December 1st, World AIDS Day 2023, we unite under the theme "Let Communities Lead," a powerful call to action emphasizing the pivotal role communities play in the global fight against HIV/AIDS. This theme recognizes that community engagement is key to effectively addressing the challenges posed by the virus and achieving the ambitious goal of ending the AIDS epidemic.
Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS) is a chronic, potentially life-threatening condition caused by the Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV). HIV weakens the immune system, making individuals susceptible to infections and diseases. Transmitted through unprotected sexual intercourse, contaminated blood transfusions, and needle sharing, AIDS has claimed millions of lives worldwide.
Despite advancements in treatment and prevention, there is no cure for AIDS. Early detection and antiretroviral therapy can manage the virus, prolonging life expectancy. Public awareness, safe practices, and accessible healthcare remain crucial in the global fight against AIDS, emphasizing the importance of education and combating stigma associated with the disease.
PRECAUTIONS
1. Safe Sex Practices: Always use condoms during sexual activity, as this significantly reduces the risk of HIV transmission.
2. Know Your Partner's HIV Status: Communicate openly with your partner about their HIV status, and encourage regular testing for both partners.
3. Avoid Sharing Needles: If you use needles for any reason, such as drug use or medical treatment, never share them to prevent the transmission of HIV through contaminated blood.
4. Screen Blood Products: Ensure that blood and blood products used for transfusions or medical procedures are properly screened for HIV.
5. Mother-to-Child Transmission Prevention: Pregnant women with HIV should seek medical advice to prevent transmission to their infants, often through antiretroviral therapy.
6. Regular Testing: Get tested for HIV regularly, especially if engaging in risky behaviors or if you are in a high-risk demographic.
7. Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis (PrEP): For individuals at high risk of HIV, consider taking PrEP medications as prescribed by a healthcare professional.
8. Education and Awareness: Stay informed about HIV/AIDS through reliable sources to understand the risks and preventive measures.
9. Cautious Tattoo and Piercing Procedures: Ensure that needles and other equipment used for tattoos or piercings are sterile to prevent the transmission of HIV.
10. Combat Stigma: Encourage an environment of understanding and support, reducing stigma associated with HIV/AIDS, which can hinder testing and treatment efforts.
Communities are the backbone of the response to HIV/AIDS, offering crucial support to those affected and driving initiatives that promote prevention, treatment, and awareness. By acknowledging and empowering communities, we recognize their resilience, dedication, and unique insights that can shape more effective and inclusive strategies.
In 2023, as we reflect on the progress made and the work that lies ahead, it is evident that communities have been at the forefront of the response. From grassroots organizations to local support networks, communities have played a vital role in ensuring that the most vulnerable have access to education, testing, treatment, and care.
This year's theme challenges us to listen to the voices of those on the ground, to understand the specific needs of different communities, and to involve them in decision-making processes. By letting communities lead, we ensure that interventions are culturally sensitive, contextually relevant, and have a lasting impact.
The COVID-19 pandemic has underscored the importance of community-led responses in times of crisis. It has also highlighted the existing health disparities that impact marginalized communities disproportionately. World AIDS Day 2023 serves as a reminder that an inclusive and community-driven approach is essential not only for the HIV/AIDS response but for building resilient healthcare systems globally.
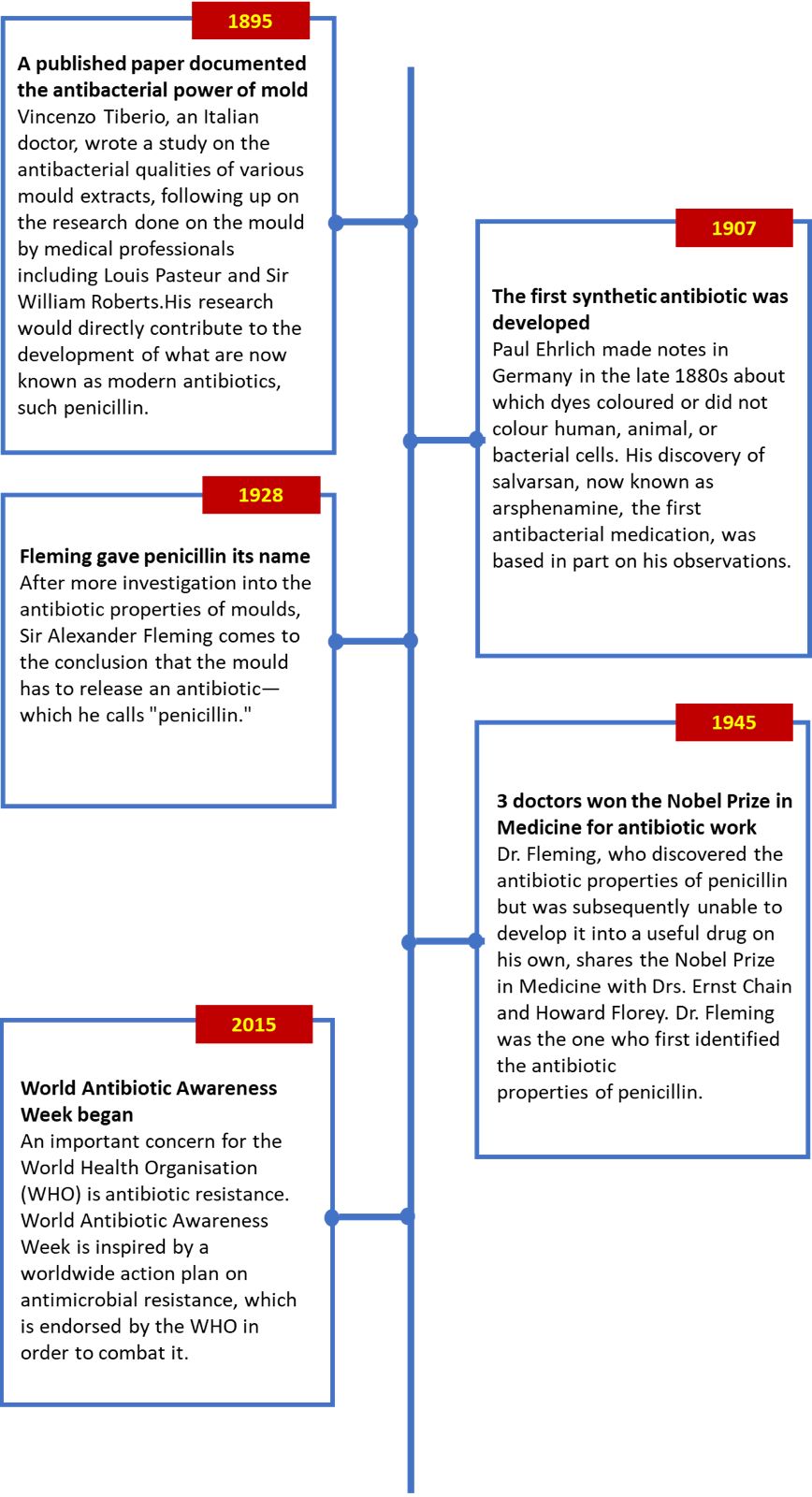
As we commemorate this day, let us celebrate the strength of communities, honor those who have been at the forefront of the fight against HIV/AIDS, and commit to supporting community-led initiatives. By empowering communities, we take a significant step towards a world where HIV/AIDS is no longer a global health threat, and every individual can access the care and support they need.Every November 18–24, World Antibiotic Awareness Week brings antibiotic resistance to our attention and highlights the efforts of the medical community to educate people on how to use these life-saving medications properly. According to the World Health Organisation (WHO), the bacterial reaction to antibiotic usage results in antibiotic resistance. Antibiotic-resistant bacteria develop this resistance, not people or animals.
HISTORY
The worldwide problem of antibiotic resistance is being handled with haste by the World Health Organisation (WHO), and for good cause. You run the risk of dying if you get sick or infected and the conventional antibiotic treatment doesn't work. It really is that easy.
According to WHO, this is a global issue that is becoming worse as a result of poverty-related diseases and infections that are becoming more and more resistant to medications. The World Health Assembly elevated the issue of antibiotic resistance to a global emergency in May 2015. "New resistance mechanisms are emerging and spreading globally, threatening our ability to treat common infectious diseases," the World Health Organisation said in describing the issue. As antibiotics lose their effectiveness, an increasing number of infections, including gonorrhoea, pneumonia, TB, blood poisoning, and foodborne illnesses, are become tougher and occasionally untreatable to treat.
The World Health Organisation (WHO) set forth five objectives concerning the issue of global antibiotic resistance: boosting awareness, stepping up monitoring and research, decreasing infections, optimising the use of antimicrobial drugs, and pledging "sustainable investment."
Most crucially, these objectives created a framework for antibiotic resistance that other countries could use to prioritise and allocate resources for medical professionals and researchers. National action plans were to coordinate with international efforts to develop antimicrobial drugs for improved animal health and application in agriculture, in addition to reducing antibiotic resistance in humans. By 2017, countries were expected to provide updates to the WHO health assemblies. Since then, the growing issue of antibiotic resistance has received more local and worldwide media attention.
WORLD ANTIBIOTIC AWARENESS WEEK TIMELINE
 KEY FACTORS ABOUT ANTIBIOTIC RESISTANCE
KEY FACTORS ABOUT ANTIBIOTIC RESISTANCE
- The issue of antibiotic resistance is worldwide.
It's crucial to keep in mind that, regardless of where we live or how sophisticated our medical training and practises may be, everyone has the potential to be impacted during World Antibiotic Awareness Week.
- Natural evolution leads to the development of antibiotic resistance.
When bacteria are exposed to an antibiotic, the more resistant ones survive and can pass on their increased resistance to their progeny, while the weaker bacteria are destroyed.
- Inappropriate usage of antibiotics can lead to resistance.
If you don't understand how to take your medication, make sure to consult your doctor. Merely taking antibiotics in the incorrect dosage (either too much or too little) might raise the potential of resistance by not successfully treating the illness.
- Medicines of poor quality may increase resistance.
Worldwide, there is often no quality control for pharmaceuticals. When subpar treatments are used, they could not be as successful in curing bacterial infections as they should be, which increases the likelihood that the illness will spread.
- Antibiotic resistance can be decreased with improved infection prevention and management.
Contrary to popular belief, hospitals consistently contribute to the issue of antibiotic resistance because hospitalised patients with infectious conditions can spread germs to other patients, increasing the risk of resistance developing. This is true despite hospitals' strict sterile procedures.The Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) collaborates with global COPD patient groups and medical experts to organise World COPD Day. The topic for the 2023 World COPD Day, which falls on November 15th, is "Breathing is Life - Act Earlier."
Never has it been more crucial to prioritise lung health! We don't appreciate our lungs enough. Your lungs are essential to our survival, thus taking care of them should be your first priority. Avoiding tobacco products, air pollution, and occupational exposures, along with maintaining an active lifestyle through pulmonary rehabilitation or regular exercise, can all help maintain healthy lungs. Furthermore, maintaining a strong immune system, attending doctor's appointments, and taking prescription drugs as directed can all contribute to lung health.
What is COPD?
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or COPD, is a long-term illness marked by restricted airways and difficulty breathing out, which traps air in the lungs. characterised by coughing up phlegm, wheezing, chronic and worsening dyspnea.
Chronic: refers to a persistent and long-lasting ailment.
Obstructive: the airways are constricted, making it more difficult to exhale rapidly and causing trapped air in the chest
Pulmonary: it has an impact on the lungs
Disease: This is a health issue
What causes COPD?
Long-term exposure to irritants that harm the lungs and airways is often the cause of COPD. Inhaled irritant exposure may be a contributing factor to COPD. These include dust or chemical vapours from the job or surroundings, air pollution, and secondhand smoking. The primary cause of COPD is tobacco use. In places like New Delhi, Mumbai & Kolkata, the prevalence of COPD is increasing due to poor air quality. Additionally, commonplace items like mosquito repellent coils used at home have been linked to COPD; a single night's exposure to these products is comparable to smoking 100 cigarettes.
Symptoms of COPD
The onset of severe lung damage triggers the onset of COPD symptoms, which often worsen over time, particularly if smoking continues. Wheezing, chest tightness, breathing problems, respiratory infections, exhaustion, inadvertent weight loss, and swelling in the ankles, feet, and legs are some of the symptoms of COPD. Furthermore, a few symptoms can be Covid-19 overlapping. Therefore, it's crucial to see a doctor in order to get a proper diagnosis. Daily tasks will often become more difficult as the symptoms worsen over time, however medication can help reduce the course.
How is it diagnosed?
In order to diagnosis chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), which encompasses emphysema and chronic bronchitis, medical practitioners will assess symptoms and obtain a full medical history from their patients based on spirometry (lung function tests), risk factors, and symptoms.
How is COPD treated?
The two primary pharmacological medications employed are inhaled corticosteroids and bronchodilators. Depending on the kind of COPD, different medication combinations are employed. Most prescriptions for the medications are for inhalation forms (nebulization, inhalers). For the treatment of severe COPD, there are currently surgical alternatives such as enhanced bronchoscopic procedures and lung volume reduction surgery (LVRS).
What can you do to manage your COPD?
When you have chronic bronchitis, there are several therapies that can improve your quality of life. It combines prescription treatments, exercise, and alterations in lifestyle.
Regular exercise and movement can enhance your fitness, breathing, and overall quality of life. Breathlessness-inducing activities shouldn't be avoided. By building muscle, regular exercise can help reverse this.
Breathing Control: There are postures and techniques that can help you feel more in control of your breathing and help you deal with shortness of breath. See your respiratory physiotherapist or nurse to determine what is most effective for you.
A balanced diet and appropriate weight Your body gets the nutrients it needs from a balanced diet to function properly and stay at a healthy weight. If required, your doctor or nurse can assist you in determining what your healthy weight is and recommend you to a local programme or dietician.
Emotional well-being: A vital component of general health is emotional wellness. Individuals who have been hospitalised, have low oxygen levels, or have more severe COPD are more likely to experience anxiety and sadness. You can get treatment to help you. Numerous more people have recovered from anxiety and sadness. Both of those are perfectly typical responses to having COPD. Consult a medical practitioner regarding prescription drugs and counselling.
How to keep your lungs healthy?
The greatest medication is prevention, and maintaining lung health is far more effective than attempting to restore them after anything goes wrong. Avoiding tobacco products, air pollution, and occupational exposures, along with maintaining an active lifestyle through pulmonary rehabilitation or regular exercise, can all help maintain healthy lungs. Furthermore, maintaining a strong immune system, attending doctor's appointments, and taking prescription drugs as directed can all contribute to lung health.
- In 1980, there were 108 million persons with diabetes; by 2014, there were 422 million. Compared to high-income countries, the prevalence has been growing more quickly in low- and middle-income nations.
- Diabetes is a leading cause of lower limb amputation, heart attacks, strokes, blindness, and renal failure.
- Age-specific diabetes death rates increased by 3% between 2000 and 2019.
- An estimated 2 million fatalities were attributed to diabetes and renal disease in 2019.
- A normal body weight, regular exercise, a balanced diet, and quitting smoking are all strategies to stop or postpone the onset of type 2 diabetes.
- Diabetes can be managed with diet, exercise, medication, and routine screening and treatment for complications to either prevent or postpone its consequences.
In 1991, the World Health Organisation and the IDF established World Diabetes Day (WDD) in response to rising concerns about the diabetes's increasing danger to health. With the adoption of UN Resolution 61/225 in 2006, World Diabetes Day was recognised as an official UN holiday. Every year on November 14th, the birthday of Sir Frederick Banting—who, in 1922, co-discovered insulin with Charles Best—is observed.
WDD is the biggest diabetes awareness campaign in the world, reaching more than 160 countries and more than 1 billion people worldwide. The campaign maintains diabetes firmly in the public and political limelight by bringing attention to topics that are extremely important to the diabetic community.
The campaign for World Diabetes Day seeks to be the:
- Platform to support IDF's year-round advocacy initiatives.
- Worldwide motivator to emphasise the significance of adopting coordinated and concerted measures to address diabetes as a serious worldwide health concern
The blue circle emblem for the campaign was chosen in 2007 following the UN Resolution on diabetes's passage. The worldwide emblem for diabetes awareness is the blue circle. It represents the solidarity of the worldwide diabetes community in the face of the diabetes pandemic.
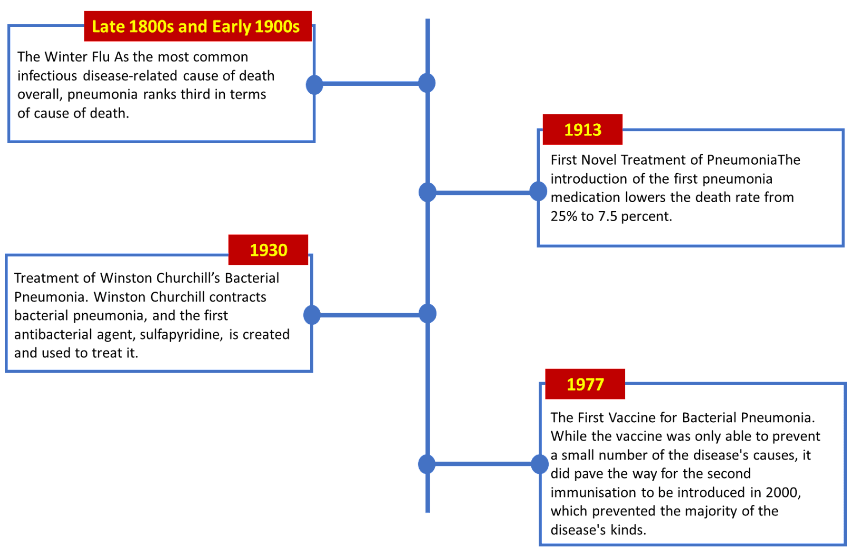
The World Diabetes Day campaign has a designated topic that is promoted for one or more years every year. “Access to Diabetes Care” is the subject for World Diabetes Day (2021–2023).November 12 is World Pneumonia Day. As with previous years, its purpose is to raise public awareness of the need for unity and demand action in the battle against this illness. The leading infectious disease that kills both adults and children worldwide is pneumonia. Its death rate alone kills more children on average than the combined rates of AIDS, measles, and malaria. The insufficiency of oxygen in the lungs highlights the significance of oxygen to our bodies and underscores the global importance of lung health. We are excited to join together on this World Pneumonia Day to discuss the importance of oxygen to human health and possible interventions to prevent pneumonia. World Pneumonia Day is especially important since that respiratory conditions are so common.
HISTORY
2009 was the inaugural World Pneumonia Day, which was marked by the Global Coalition against Child Pneumonia. Their goals were to raise public awareness of the severity of pneumonia and to work together to draw attention to this often-ignored illness on a worldwide scale. "Healthy Lungs for Everyone" served as the day's overarching theme and has been since the inaugural World Pneumonia Day in 2009. The slogan was expanded to incorporate other words related to conducting campaigns, such as providing adequate protection against the disease and facilitating treatment centre accessibility for those afflicted with it.
About 1.2 million children died from pneumonia in the year that the inaugural World Pneumonia Day was marked. An Integrated Global Action Plan for the Prevention and Control of Pneumonia and Diarrhoea was introduced by WHO and UNICEF in 2013—four years after this day was first observed on a worldwide and international level. The first public-private partnership to assist governments in implementing the Global Action Plan for Pneumonia and Diarrhoea (G.A.P.P.D.) was created under the moniker "Every Breath Counts" throughout the course of the following four years in an attempt to establish as much control over the diseases as possible.
Apart from this, a number of additional measures have also been implemented at different degrees to combat the assaults of pneumonia, which continues to be the leading cause of infectious mortality among both adults and children.
WORLD PNEUMONIA DAY TIMELINE
 5 FACTS ABOUT PNEUMONIA EVERYONE SHOULD KNOW
5 FACTS ABOUT PNEUMONIA EVERYONE SHOULD KNOW
-
A single cause does not exist for pneumonia.
According to scientists and medical professionals - bacteria, fungus, or both at the same time, can cause pneumonia. It can also be brought on by inhaling dust, breathing in food, or breathing in any little poison in the air that might harm a person's health.
-
Breastfeeding supports the defence against it.
According to medical professionals, children who consumed mother's milk on a daily basis had higher immunity, which increased their chances of fending against pneumonia and recovering from it even in the event that they were sick.
-
Pneumonia killed 15% of children in 2017.
It is estimated that the epidemic claimed the lives of 808,694 children, or 15% of all children under five who perished.
-
There are over thirty distinct causes of pneumonia.
Fungi, bacteria, or potentially both can cause pneumonia, but identifying the underlying cause is essential to a successful course of therapy.
-
lung health is gravely endangered
Globally, the total number of pneumonia cases has increased by 75% recently.The World Hepatitis Alliance reports:
-
- The most typical cause of hepatitis, an inflammation of the liver, is a viral infection.
- Hepatitis viruses come in five different types: A, B, C, D, and E.
- The burden of sickness and mortality they bring along with the potential for breakouts and epidemic transmission make these five varieties the most concerning.
- A viral hepatitis-related disease claims the life of a person every 30 seconds. It is crucial to get evaluated and undergo treatment in light of the current preventative measures.
Every year on 28 July, the globe comes together under the banner of globe Hepatitis Day (WHD) to raise awareness of the burden of viral hepatitis across the world and to effect lasting change. Our theme for this year is "We're not waiting." "Accelerate viral hepatitis elimination efforts now and the urgent need for testing and treatment for the real people who need it," reads the WHD 2023 call to action. Around the world, people and communities are bringing about change in their own lives and the environment. While praising them, we call for further action. WHD is one of only four disease-specific global awareness days that the World Health Organisation (WHO) has formally recognised. To raise awareness of viral hepatitis worldwide, WHD brings together patient organisations, governments, medical specialists, civil society, business, and the general public.
Why should we acknowledge World Hepatitis Day?
One of the main causes of death worldwide, viral hepatitis causes 1.34 million deaths annually, more than HIV/AIDS, TB, or malaria combined. 80% of liver cancer cases worldwide are caused by the hepatitis B and C viruses when they are combined.
Viral hepatitis is a really worldwide disease that can infect millions of people without their knowledge. It is not just present in one place or among one group of individuals.
90% of those with hepatitis B and 80% of those with hepatitis C do not now know their condition. Due to this, there is a significant chance that they may have deadly liver illness at some time in their life and, in some situations, unintentionally spread the infection to others.
The eradication of viral hepatitis is feasible because to the availability of effective hepatitis B vaccinations, treatments, and a cure, as well as a therapy for hepatitis C. However, increased knowledge of the illness, its hazards, and access to less expensive diagnostics and treatment are required. We are at a turning point in the fight against viral hepatitis thanks to the inclusion of the disease in the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and the recent approval of the first global hepatitis strategy. The need for political commitment is more than ever. Without prompt intervention, the number of fatalities and the spread of the disease would both increase.
The occasion provided by World Hepatitis Day is appropriate for raising awareness of viral hepatitis among the general public, in the media, and on the global health agenda. Viral hepatitis must be eradicated right away.
DIPHTHERIA often spreads through the air. Fever, throat discomfort, and neck swelling are the symptoms. Breathing difficulties may develop in severe situations. It can result in heart failure and paralysis days after the infection. The majority of reported cases of diphtheria worldwide are in India.
Whooping cough, also known as PERTUSSIS, is an airborne illness. Coughing follows, and it lasts for 4-6 weeks. Extreme coughing fits can make it difficult to breathe and to eat or drink. All age groups are susceptible, with very young newborns suffering the most severe effects. It may result in mortality, pneumonia, seizures, or brain damage.
Contaminated wounds can lead to TETANUS, which can also develop in a newborn after risky delivery procedures. It is commonly referred to as "lockjaw" because it produces excruciating muscular spasms and the difficulty to swallow.
The DPT vaccination guards against tetanus, diphtheria, and whooping cough (pertussis).
AVAILABILITY
DPT (Triple antigen), DPT/Hib (Quadrivalent), DPT/HBV/Hib (Pentavalent), and DPT/HBV/Hib/IPV (Hexavalent) are the combinations of these vaccinations that are available. Some vaccines intended for use in adults and children older than 7 years old combine a full dose of tetanus with a reduced dose of components for diphtheria and pertussis. These are, respectively, the Tdap and Td vaccines.
SCHEDULE OF DPT VACCINES
- Three doses are given at 6-10-14 weeks of age in the first year, one booster at 16-18 months in the second year, and two boosters at 4-6 years of age. They are given in conjunction with Hepatitis B, Hib, and IPV vaccinations that are age-appropriate.
- At 10 to 12 years old, adolescents should also receive one dose of the Tdap vaccine.
- After then, Td is advised every 10 years.
- Every pregnancy should include one dose of Tdap (or, as a backup option, the Td vaccination) administered between weeks 27 and 36.
- After skin-breaching wounds or trauma, tetanus prophylaxis with the td vaccination is also employed.
The hepatitis B vaccination can guard against the disease. Hepatitis B is a liver condition that can result in a short-lived, moderate sickness or a severe, chronic condition.
- Short-term acute hepatitis B infection symptoms include fever, exhaustion, appetite loss, nausea, vomiting, jaundice (yellow skin or eyes, dark urine, clay-colored stools), and pain in the muscles, joints, and stomach.
- When the hepatitis B virus persists in a person's body for an extended period of time, they develop chronic hepatitis B infection. The majority of persons who go on to acquire chronic hepatitis B do not exhibit any symptoms, yet the condition is nonetheless highly hazardous and can result in death, liver cancer, and liver damage (cirrhosis). Even though they do not themselves seem or feel ill, those who have a chronic infection can nevertheless transmit the hepatitis B virus to others.
When blood, semen, or other bodily fluid containing the hepatitis B virus enters the body of a person who is not afflicted, hepatitis B is transmitted. People may get an infection by:
- Birth (a pregnant person with hepatitis B risks infecting their unborn child)
- Sharing objects like toothbrushes or razors with an infected individual
- contact with an infected person's blood or open sores
- Sex with a partner who is infected
- Sharing syringes, needles, or other drug injection tools
- exposure to blood through the use of needles or other sharp objects
The majority of persons who receive the hepatitis B vaccination are permanently immune.
The standard dosage for the hepatitis B vaccination is 2, 3, or 4.
- Hepatitis B vaccination for infants should begin at birth, with the final dose given between 6 and 18 months of age. An essential component in stopping children' long-term illnesses and the spread of hepatitis B in the US is the birth dose of the hepatitis B vaccine.
- All children and teenagers under the age of 19 who have not received the vaccination yet should do so.
- The vaccine is also available for adults who wish to be protected against hepatitis B but have never had a vaccination.
The following individuals are also advised to have the hepatitis B vaccine:
- people who have hepatitis B in their sex relationships
- People who are sexually active but not in a committed, monogamous relationship Those seeking testing or treatment for an STD
- sexual assault or abuse victims
- males who interact romantically with other males
- People who reside with someone who has the hepatitis B virus People who share needles, syringes, or other drug-injection supplies
- Public safety and healthcare employees who may be exposed to blood or bodily fluids
- Residents and employees of developmentally handicapped facilities
- Those who are incarcerated or in prison Visitors to areas with higher hepatitis B infection rates
- People with HIV, hepatitis C, chronic liver disease, and renal disease who are on dialysis
Hepatitis B vaccine can be administered as a standalone injection or as a component of a combination vaccination, which is a form of vaccine that contains multiple shots of different vaccines.
The hepatitis B vaccination may be administered concurrently with other shots.
 KEY FACTORS ABOUT ANTIBIOTIC RESISTANCE
KEY FACTORS ABOUT ANTIBIOTIC RESISTANCE
 5 FACTS ABOUT PNEUMONIA EVERYONE SHOULD KNOW
5 FACTS ABOUT PNEUMONIA EVERYONE SHOULD KNOW