World Diabetes Day 2022
12 November, 2022
Diabetes is a chronic (long-lasting) health condition that affects how your body turns food into energy.
Your body breaks down most of the food you eat into sugar (glucose) and releases it into your bloodstream. When your blood sugar goes up, it signals your pancreas to release insulin. Insulin acts like a key to let the blood sugar into your body cells for use as energy.
With diabetes, your body doesn't make enough insulin or can't use it as well as it should. When there isnot enough insulin or cells stop responding to insulin, too much blood sugar stays in your bloodstream. Over time, that can cause serious health problems, such as heart disease, diabetes, vision loss, and diabetes-kidney-disease.
There isn't a cure yet for diabetes, but losing weight, eating healthy food, and being active can really help. Other things you can do to help:
Take medicine as prescribed.
Getdiabetes self-management education and support.
Make and keep health care appointments.
Types of Diabetes
There are three main types of diabetes:
type 1, type 2, and
gestational diabetes (diabetes while pregnant).
1 Diabetes
diabetes is thought to be caused by an autoimmune reaction (the body attacks itself by mistake). This reaction stops your body from making insulin. Approximately 5-10% of the people who have diabetes have type 1. Symptoms of type 1 diabetes often develop quickly. It's usually diagnosed in children, teens, and young adults. If you have type 1 diabetes, you'll need to take insulin every day to survive. Currently, no one knows how to prevent
2 Diabete
With type 2 diabetes, your body doesn't use insulin well and can't keep blood sugar at normal levels. About 90-95% of people with diabetes have type 2. It develops over many years and is usually diagnosed in adults (but more and more in children, teens, and young adults). You may not notice any symptoms, so it's important to get your blood sugar tested if you're at
risk. Type
2 diabetes can be prevented or delayed with healthy lifestyle changes, such as:
Losing weight.
Eating healthy food.
Being active.
Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes develops in pregnant women who have never had diabetes. If you have gestational diabetes, your baby could be at higher risk for health problems. Gestational diabetes usually goes away after your baby is born. However, it increases your risk for type 2 diabetes later in life. Your baby is more likely to have obesity as a child or teen and develop type 2 diabetes later in life.
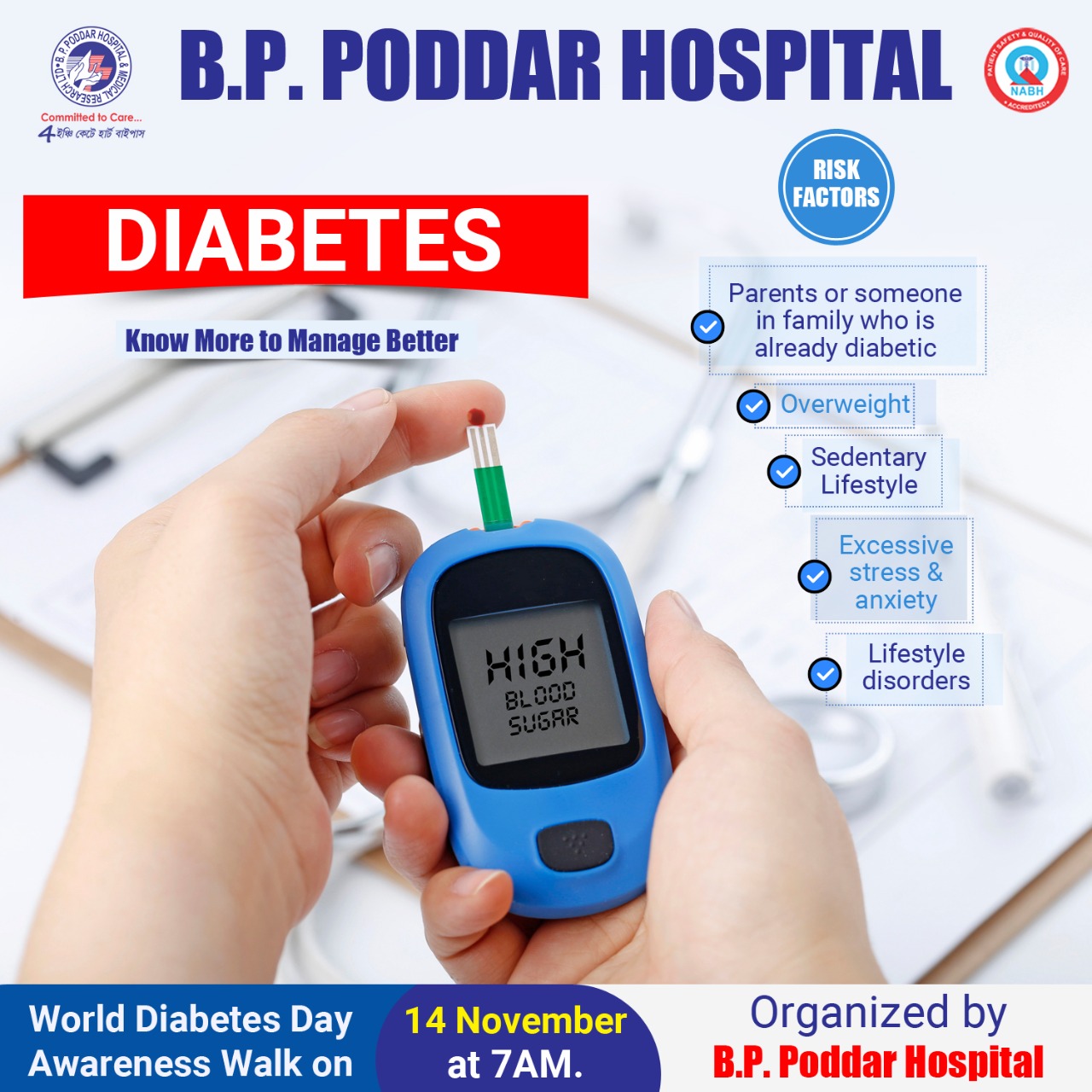
Diabetes Risk Factors
Diabetes is thought to be caused by an immune reaction (the body attacks itself by mistake). Risk factors for type 1 diabetes are not as clear as for prediabetes and type 2 diabetes. Known risk factors include:
Family history:
Having a parent, brother, or sister with type 1 diabetes.
Age: You can get type 1 diabetes at any age, but it usually develops in children, teens, or young adults.
Currently, no one knows how to prevent type 1 diabetes.
Diabetes
You're at risk for type 2 diabetesif you:
Have prediabetes.
Are overweight.
Are 45 years or older.
Have a parent, brother, or sister with type 2 diabetes.
Are physically active less than 3 times a week.
Have ever had gestational diabetes (diabetes during pregnancy) or given birth to a baby who weighed over 9 pounds.
If you have non-alcoholic fatty liver disease you may also be at risk for type 2 diabetes.
You can prevent or delay type 2 diabetes with proven lifestyle changes. These include losing weight if you're overweight, eating a healthy diet, and getting regular get-moving-to-manage-diabetes. physical activity
Symptoms of Diabetes
If you have any of the following diabetes symptoms, see your doctor about getting your
blood sugar tested.
Urinate (pee) a lot, often at night
Are very thirsty
Lose weight without trying
Are very hungry
Have blurry vision
Have numb or tingling hands or feet
Feel very tired
Have very dry skin
Have sores that heal slowly
Have more infections than usual
Symptoms of ] Diabetes
1. People who have may also have nausea, vomiting, or stomach pains. Type 1 diabetes symptoms can develop in just a few weeks or months and can be severe. Type 1 diabetes usually starts when you're a child, teen, or young adult but can happen at any age.
2. diabetes often take several years to develop. Some people don't notice any symptoms at all. Diabetes usually starts when you're an adult, though more and more children and teens are developing it. Because symptoms are hard to spot, it's important to know the
risk factors for type 2 diabetes. Make sure to visit your doctor if you have any of them.
Diabetes Prevention
Can Type 2 Diabetes Be Prevented?
Yes! You can prevent or delay type 2 diabetes with proven, achievable lifestyle changes; such as losing a small amount of weight and getting more physically active even if you're at high risk. Read on to find out about lifestyle change program and how you can join.
What is Prediabetes?
Before developing type 2 diabetes, most people have prediabetes; their blood sugar is higher than normal but not high enough yet for a diabetes diagnosis. Prediabetes is really common. The good news is that prediabetes can be reversed.
DOs and DONTs in Diabetes
DOs if you have diabetes
Proper diet, regular exercise and meditation are important.
Eat small and frequent meals. Control portion size; don't give long gap between meals. Have early dinner.
Include raw or fresh salads and high fibre food (wheat, ragi, jowar, millets and brans) in every meal.
Include green leafy vegetables and sprouts, flax seeds, chia seeds daily.
Selected fruits like small apple, pear (marasebu), orange, guava, peaches, sweet-lime, plum, 1 slice muskmelon, apricot, jamun, papaya and pineapple are allowed 100gms only and preferably in midmorning if the fasting blood glucose levels are less than 100mg/dl.
Use boiling/steaming/baking/grilling process for cooking food.
Limit the salt intake to 5gm/day or one leveled teaspoon.
For cooking, use rice-bran oil, canola oil, groundnut oil, mustard oil, sunflower oil, olive oil etc. and limit the intake to 500 Gms or half a liter per person per month.
Include plenty of water, buttermilk, soups and keep your self-hydrated.
DON'Ts if you have diabetes
Cut down refined carbs like sweets and sweetened products like sugar, honey, jaggery, cakes, pastries etc.
Avoid fried foods butter/nutralite, Vanaspati and coconut.
Avoid sweetened fruit juice, high calorie fruits or overripe fruits like mango, banana, sapota, seethaphal and jackfruit.
Avoid roots and tubers such as potato, sweet potato, beetroot, yam, tapioca and sweet pumpkin.
Avoid aerated and caffeinated drinks such as pepsi, coke, fanta, diet coke, soda etc.
Avoid dry fruits such as raisins, dates, figs, prunes, plums, cashew and pista.
Restrict the amount of salt in the diet. Avoid papad, pickles, processed food, canned food, baking soda and aginomoto.
Artificial sweeteners like Sugarfree can be used with tea and coffee in small amounts.
Avoid organ meat, red meat (mutton), beef, pork, and egg-yolk.
Strictly avoid health drinks.
